El Niño: The Who, the What, and How It Affects Us
While this summer has had its heat waves, forecasters are anticipating further rising temperatures to round out the second half of 2023. Not only will this affect temperatures, but we can anticipate even hotter temperatures in 2024.
But…why? This is due to El Niño, a climatic phenomenon, that emerges as a result of periodic warming in sea surface temperatures within the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean. This occurrence is irregular, typically taking place every two to seven years, and persisting for approximately 9 to 12 months. El Niño plays a pivotal role in shaping global weather patterns, exerting its influence through intricate interactions between oceanic and atmospheric systems.
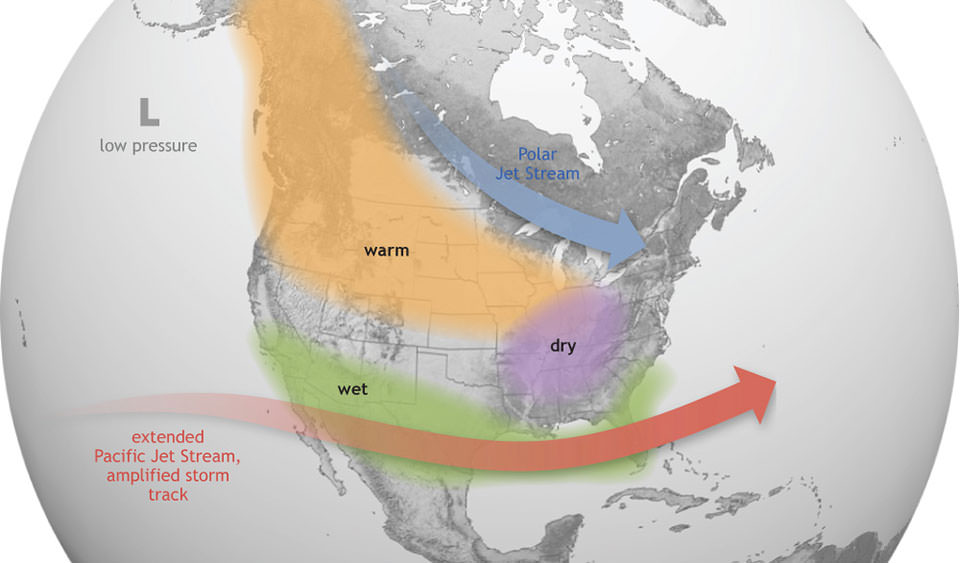
How does this affect us, especially those of us on the East Coast? For some of the US and Canada, El Niño means drier, hotter temperatures. For those towards the Gulf, El Niño creates wetter conditions, including flooding.
All in nature has a cause and effect; El Niño is no different. To counter this, there is La Niña, which pushes cooler water out. For us in the Northeast, it means cooler winter temperatures; for those in the South, it means warmer temperatures and a risk of stronger hurricanes.
While El Niño and La Niña are opposing climate patterns, they both can last on average a year. The reverberations of El Niño and La Niña extend beyond localized weather alterations, influencing global economic factors. These climatic fluctuations can impact oil and gas prices, spurred by fluctuations in heating and cooling demand.
🌊 El Niño Unveiled: A natural climate phenomenon that arises from warming Pacific waters every 2-7 years, impacting weather worldwide for around 9-12 months.
🌡️ Temperature Shifts: Warming eastern Pacific triggers heatwaves in regions, affecting ecosystems, agriculture, and our health.
☔ Rainfall Changes: El Niño alters precipitation patterns—less rain on US West Coast, more along the Gulf, leading to floods.
❄️ La Niña’s Role: The cooler counterpart to El Niño, influencing weather oppositely in the ENSO cycle.
💼 Global Reach: Beyond local weather, El Niño affects economies, driving shifts in oil and gas prices due to heating and cooling demands.
🌍 Climate Complexity: El Niño’s part of a broader climate picture alongside long-term change.
Written by: Michelle & Nicholas
Sources & Photo: NOAA






Leave A Comment